CH32V003 (SOP-8) Arduino Pin Remapping & Serial Guide
Overview
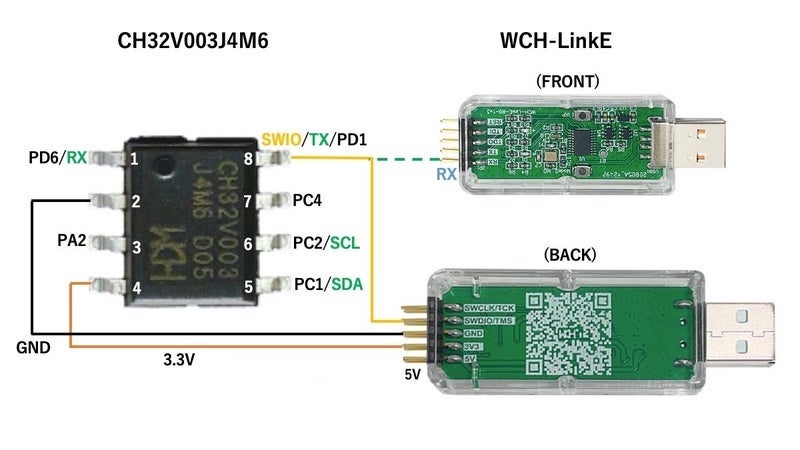
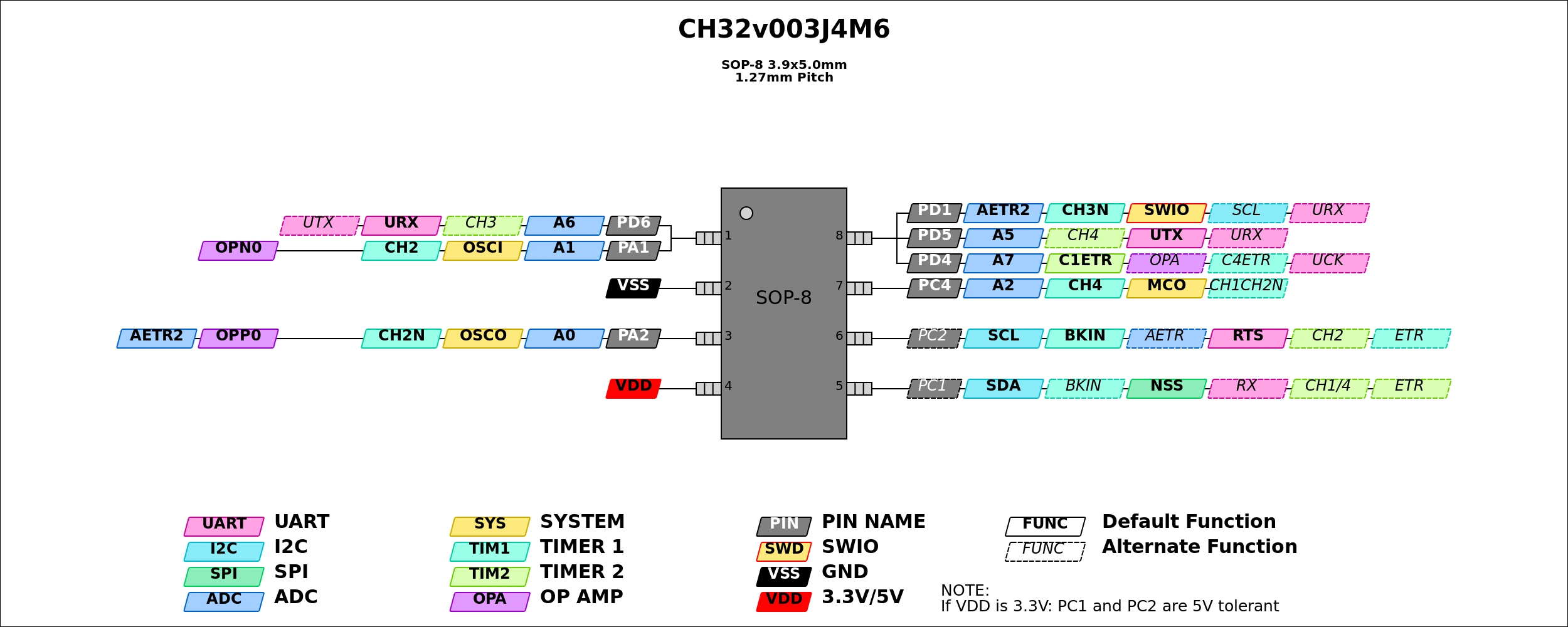
The CH32V003J4M6 comes in a tiny SOP-8 package. Due to the limited pin count (only 6 usable I/O pins), standard Arduino pin mappings often conflict with required peripherals like I2C or the SWIO programming interface.
This guide details how to:
- Remap Hardware Serial to different pins by modifying the Arduino Core.
- Manage Conflicts (e.g., losing I2C to gain Serial RX).
- Share Pin 8 (SWIO) for both programming and Serial TX.
- Unbrick/Erase the chip using
minichlinkif configuration errors lock you out.
The Pinout Constraints
On the SOP-8 package, several peripherals share the same physical pins. You cannot use all functions simultaneously.
| Pin # | Pin Name | Default Function | Conflict / Alt Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PD6 | UART1 RX (Default) | Can be remapped to UART1 TX |
| 5 | PC1 | I2C SDA | Can be remapped to UART1 RX |
| 6 | PC2 | I2C SCL | - |
| 8 | PD1 | SWIO (Programming) | Can be remapped to UART1 TX |
Method 1: Permanent Remap (Editing Core Files)
To use Hardware Serial on Pin 1 (PD6) as TX, you must modify the board definition files. This allows Serial.print to work natively on the new pins.
1. Locate the Core Files
Navigate to the directory where the WCH Arduino core is installed:
- Windows:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Arduino15\packages\WCH\hardware\ch32v\1.0.4\variants\CH32V003F4 - Linux:
~/.arduino15/packages/WCH/hardware/ch32v/1.0.4/variants/CH32V003F4 - Mac:
~/Library/Arduino15/packages/WCH/hardware/ch32v/1.0.4/variants/CH32V003F4
2. Modify PeripheralPins.c
Open PeripheralPins.c. You need to change the pin definitions in the PinMap_UART_TX and PinMap_UART_RX arrays.
To set TX to Pin 1 (PD6) and RX to Pin 5 (PC1): Note: This configuration sacrifices hardware I2C SDA on Pin 5.
//*** UART ***
#ifdef UART_MODULE_ENABLED
WEAK const PinMap PinMap_UART_TX[] = {
{PD_6, USART1, CH_PIN_DATA(CH_MODE_OUTPUT_50MHz, CH_CNF_OUTPUT_AFPP, 0, AFIO_NONE)}, // from PD_5
{NC, NP, 0}
};
#endif
#ifdef UART_MODULE_ENABLED
WEAK const PinMap PinMap_UART_RX[] = {
{PC_1, USART1, CH_PIN_DATA(CH_MODE_INPUT, CH_CNF_INPUT_PUPD, PULLUP, AFIO_NONE)}, // from PD_6
{NC, NP, 0}
};
#endif
3. Modify variant_CH32V003F4.h
Open variant_CH32V003F4.h and update the definitions to match your changes in PeripheralPins.c.
// UART Definitions
#ifndef SERIAL_UART_INSTANCE
#define SERIAL_UART_INSTANCE 1
#endif
// Default pin used for generic 'Serial' instance
// Mandatory for Firmata
#ifndef PIN_SERIAL_RX
#define PIN_SERIAL_RX PC1 // from PD6
#endif
#ifndef PIN_SERIAL_TX
#define PIN_SERIAL_TX PD6 // from PD5
#endif
Warning: These changes affect all sketches compiled for the CH32V003F4 board. If you switch projects, you may need to revert these files.
4. Modify your sketch
Add the following lines to your setup() code in your Arduino IDE sketch:
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOD | RCC_APB2Periph_USART1 | RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO, ENABLE);
GPIO_PinRemapConfig(GPIO_PartialRemap2_USART1, ENABLE);
Serial.begin(115200);
5. Full code
#define ledpin PC4
int counter = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(ledpin, OUTPUT);
// Must enable clock for AFIO
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOD | RCC_APB2Periph_USART1 | RCC_APB2Periph_AFIO, ENABLE);
GPIO_PinRemapConfig(GPIO_PartialRemap2_USART1, ENABLE);
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledpin, HIGH);
delay(80);
counter++;
digitalWrite(ledpin, LOW);
delay(300);
Serial.print("blink ");
Serial.println(counter);
}
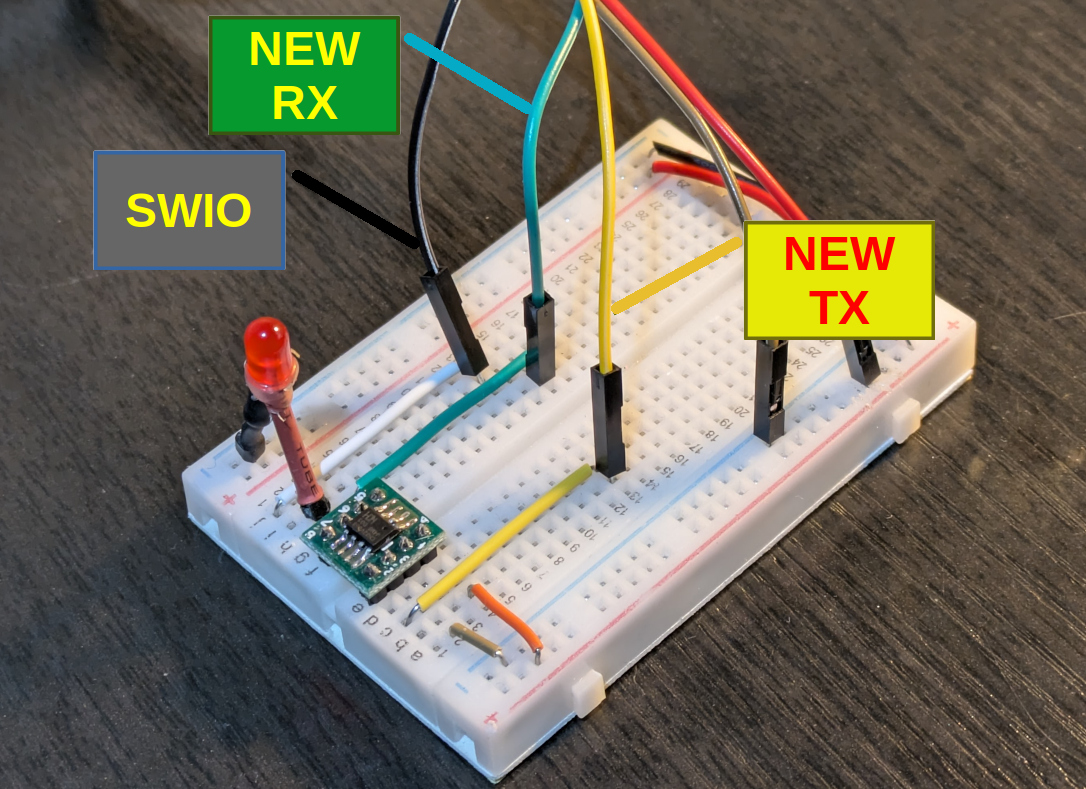
6. Switch the new RX/TX connections
Do not forget to switch to the new RX/TX pins. Then you can reprogram and use serial communication as well.
Method 2: Shared Serial on Pin 8 (SWIO)
If you need Pin 1 and Pin 5 for other uses (like sensors), you can use Pin 8 (PD1) for Serial TX. However, PD1 is the SWIO programming pin.
To use this safely, you must dynamically initialize and de-initialize the Serial port in your code. This ensures the pin is only driving data when you specifically print, leaving it free for the programmer (WCH-Link) the rest of the time.
Code Implementation
Do not put Serial.begin() in setup(). Instead, wrap your print statements like this:
void setup() {
// Do not initialize Serial here!
}
void loop() {
// 1. Initialize Serial (Claims Pin 8)
Serial.begin(115200);
// 2. Send Data
Serial.println("Battery Status: OK");
// 3. Wait for transmission to complete
Serial.flush();
// 4. End Serial (Releases Pin 8 back to High-Z/Input)
Serial.end();
// Pin 8 is now free for SWIO programming
delay(1000);
}
Pros: Keeps Pins 1, 5, and 6 free for sensors.
Cons: You cannot debug continuously; using the Serial Monitor constantly will make it difficult to upload new code.
Unbricking / Full Erasure
If you configure the pins incorrectly (e.g., setting SWIO to output low permanently) or disable the debug interface, the WCH-Link might fail to detect the chip.
To recover the chip, you need to perform a full erasure using minichlink.
Prerequisites
- Clone the cnlohr/ch32fun or openwch/ch32v003 repository.
cd ~
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/cnlohr/ch32fun.git
- Go to the directory
cd ch32fun/minichlink
- Run compile
make
In case of an error
/usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lusb-1.0: No such file or directory
collect2: error: ld returned 1 exit status
make: *** [Makefile:47: minichlink] Error 1
Install dependencies
sudo apt update
sudo apt install libusb-1.0-0-dev libudev-dev
- Install the binary
sudo cp minichlink /usr/local/bin/
Check if succesfull
which minichlink
Should output
/usr/local/bin/minichlink
- Connect the WCH-LinkE to the chip using a single wire interface (SWD).
The Unbrick Command
Run the following command in your terminal:
minichlink -u
-u: This flag commands the programmer to perform a chip erase and re-enable the SWIO interface.- If this fails, try holding the chip in "Reset" (connect NRST to GND if available, or power cycle rapidly) while issuing the command.
References & Credits
This guide describes advanced configuration techniques derived from the following resources:
- YouTube: Re-mapping the pins on a CH32v003 – Visual guide on locating and editing the Arduino Core files for pin redefinition.
- Blog: CH32v003 Serial and SWIO Communication Clash – Detailed analysis of pin conflicts on the SOP-8 package and methods for resolving SWIO/Serial overlaps.